PR testing tutorial
This tutorial is up to date as of September 29, 2024
This tutorial will guide you through testing changes made in an open pull
request in void-packages.
Prerequisites
- basic knowledge of Git
- basics of CLI
Cloning
The steps to follow differ depending on whether you already have a
void-packages clone.
- You don’t have a
void-packagesclone - You have a
void-packagesclone
You don’t have a void-packages clone
You want to try out a singe PR and never touch void-packages again
You should go to the pull request you want to test:
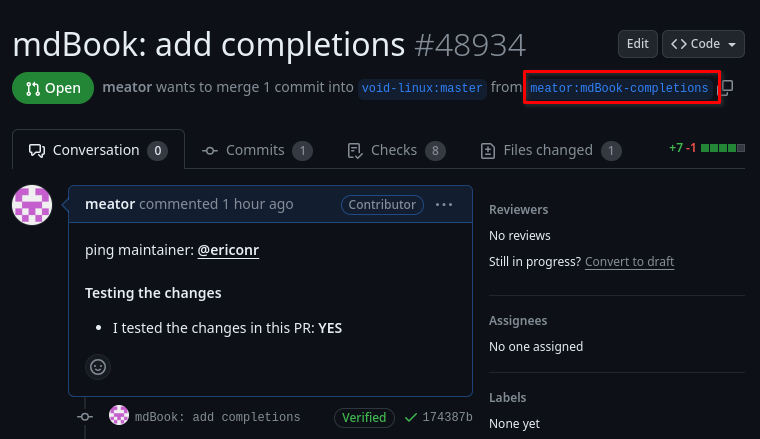
Click on the highlighted link. It will take you to the forked repository of the author of the pull request.
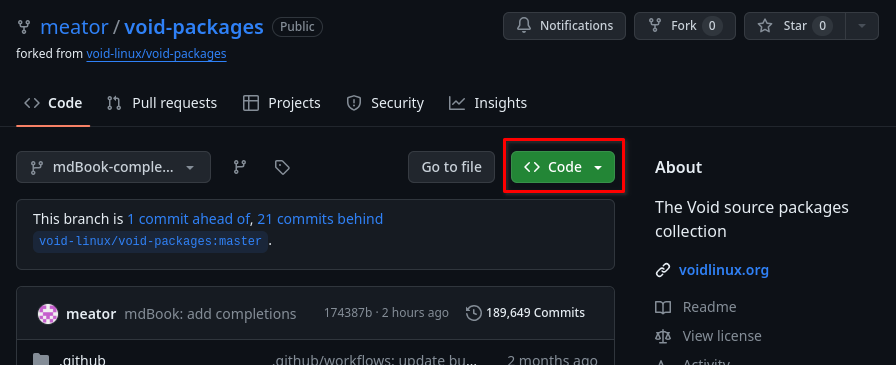
Press the Code button:
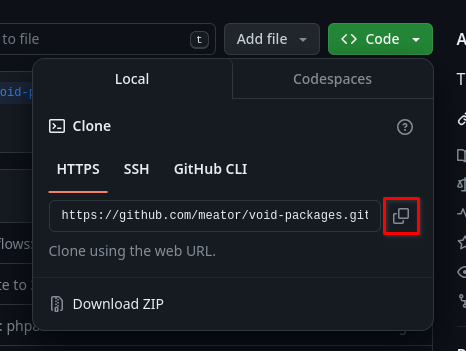
Copy the HTTPS or SSH link according to your preference (if you do not have one,
choose HTTPS):
You should also know the name of the branch from the first picture. Here it’s
mdBook-completions.
Now, clone the repo using a terminal:
# Replace these! vvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvv vvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvv
git clone --depth 1 --single-branch --branch=mdBook-completions https://github.com/meator/void-packages.git
You must replace the branch and the link with yours.
Don’t forget to enter your freshly downloaded clone:
cd void-packages
You can now continue with Setting up the builddir.
You want to have void-packages for future use
You can clone the repository with
git clone https://github.com/void-linux/void-packages.git
# or with SSH
#git clone git@github.com:void-linux/void-packages.git
This takes about 15 minutes and 626MiB on my laptop.
To speed this up, you can look at different ways of cloning. But the full clone should be preferred.
Don’t forget to enter your freshly downloaded clone:
cd void-packages
You can then continue with You have a void-packages
clone.
You have a void-packages clone
There are two ways to check out a PR: with gh or with git.
gh
This method requires github-cli to be installed.
github-cli requires authentication to your GitHub account. If you aren’t
authenticated, gh will show you instructions on how to authenticate.
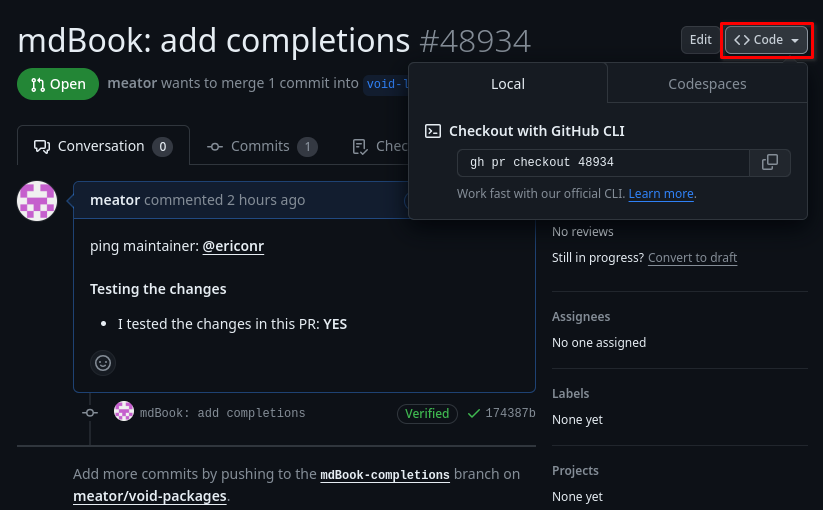
You can check out the pull request by
gh pr checkout 48934
GitHub has a handy button for that:
gh may prompt you to set the default repository when first running it. You
should select void-linux/void-packages.
git
You’ll have to figure out the pull request number. You can find it here
(excluding the leading # character):
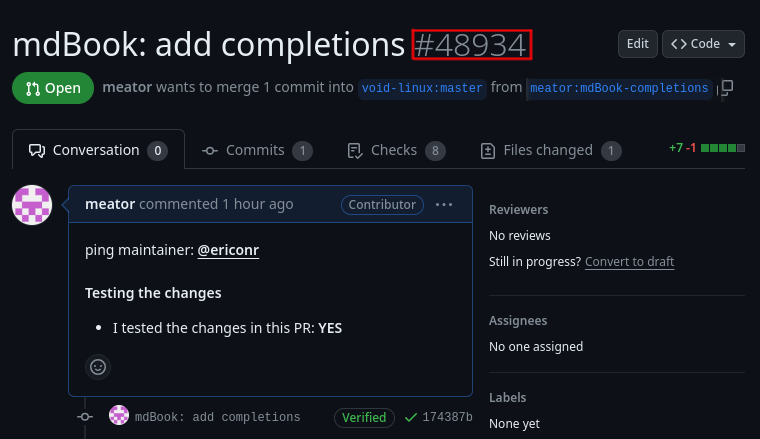
The generic process looks like this1:
git fetch upstream pull/<number>/head:<some branch name>
git checkout <some branch name>
I will showcase it on the pull request mentioned above.
You first have to add the upstream repo as a remote (if you don’t have it already):
git remote add upstream git@github.com:void-linux/void-packages.git
# Or with HTTPS:
#git remote add upstream https://github.com/void-linux/void-packages.git
Then you have to fetch the PR and check out to it. In the following sample, I’m
cloning PR number 48934 to branch mdbook-compl:
git fetch upstream pull/48934/head:mdbook-compl
git checkout mdbook-compl
Updating
Skip this section if you have followed You want to try out a singe PR and never
touch void-packages
again.
The pull request might be a bit out of date when compared to
void-packages. This can result
in problems. To update it, you must have the upstream remote. Your git remote -v should look like this (with the target fork instead of
meator/void-packages.git):
origin git@github.com:meator/void-packages.git (fetch)
origin git@github.com:meator/void-packages.git (push)
upstream git@github.com:void-linux/void-packages.git (fetch)
upstream git@github.com:void-linux/void-packages.git (push)
or like this for HTTPS:
origin https://github.com/meator/void-packages.git (fetch)
origin https://github.com/meator/void-packages.git (push)
upstream https://github.com/void-linux/void-packages.git (fetch)
upstream https://github.com/void-linux/void-packages.git (push)
If you do not have the upstream entry, you must add it:
git remote add upstream https://github.com/void-linux/void-packages.git
# Or with SSH
#git remote add upstream git@github.com:void-linux/void-packages.git
If you have the upstream entry, you can update the branch using it:
git pull --rebase upstream master
If merge conflicts arise, you’ll have to fix them or use the older version in the PR without updating it.
Setting up the builddir
Skip this if you have a builddir.
You can set up the builddir with
./xbps-src binary-bootstrap
This takes about two minutes on my laptop.
Building
You can build the package with
./xbps-src pkg <package>
here it would be
./xbps-src pkg mdBook
Installing
This requires the xtools package.
Run
sudo xi -f <package>
here it would be
sudo xi -f mdBook
And that’s it. If you don’t want to build any more packages, you can run
./xbps-pkg zap
to delete the masterdir. This can save up space.
If you only wanted to install the package and don’t care about void-packages
any more, you can remove the clone now.
Feedback
You should comment on the original pull request and share your experiences with the package. If you have encountered any problems with it, you should report them.
Taken from here.