Package update tutorial
This tutorial is up to date as of September 29, 2024
This tutorial will guide you through updating an already existing package using
xbps-src.
Prerequisites
- basic knowledge of Git
- basic knowledge of GitHub for contributing (have an account, know how to make a pull request)
- basics of CLI
This tutorial described the simple procedure of changing the version and
checksum of a template. Some updates have breaking changes that have to be
accounted for. There is no universal way to fix it, you have to figure it out.
If a simple version update won’t cut it, you’ll have to make changes to the
template. You can read the xbps-src packaging
tutorial for an in-depth explanation of templates.
This tutorial is aimed at simpler packages. You likely won’t be able to update browsers, kernels, DEs and other stuff without a great amount of work.
- Make sure that a PR isn’t open already
- Setting up
void-packagesand the masterdir - Setting up a branch
- Updating package
xlint- Making a pull request
Make sure that a PR isn’t open already
You should look in https://github.com/void-linux/void-packages/pulls and make sure that an open PR doesn’t already make the changes you want. If there is one, you should follow PR testing tutorial.
Setting up void-packages and the masterdir
Skip this section if you have everything set up.
The procedure differs depending on whether you want to contribute your changes
to void-packages or not.
If you do not want to contribute the update and you don’t plan to use
void-packages in the future,
you can clone the repo with
git clone --depth 1 https://github.com/void-linux/void-packages.git
Cloning with --depth 1 is much faster, but it doesn’t include history, which
is necessary for updating the repo and it’s useful for contributing.
If you want to use
void-packages in the future,
you should do a full clone (void-packages’
CONTRIBUTING
recommends using SSH):
git clone git@github.com:void-linux/void-packages.git
# Or this with HTTPS if you do not want to set up SSH keys:
#git clone https://github.com/void-linux/void-packages.git
A full clone takes about 15 minutes on my computer and it occupies 626M1.
If you want to contribute, you should have a fork of
void-packages set up. You should then clone it:
# Replace with your fork!vvvvvv
git clone git@github.com:meator/void-packages.git
# Or this with HTTPS if you do not want to set up SSH keys:
# Also replace with your fork!vvvvvv
#git clone https://github.com/meator/void-packages.git
You should also set up the upstream remote2:
git remote add upstream git@github.com:void-linux/void-packages.git
# Or this with HTTPS if you do not want to set up SSH keys:
#git remote add upstream https://github.com/void-linux/void-packages.git
After cloning it, you must set up a masterdir. This can be done with the
following command (after you cd into the repository):
./xbps-src binary-bootstrap
This takes about two minutes on my notebook.
You can now build packages in
void-packages using
./xbps-src pkg <package>
You can install built packages with
sudo xi -f <package>
(The xi utility is provided by the xtools package.)
Setting up a branch
You can skip this if you are making the update for personal use only. But having it in a separate branch is still useful for organisation.
Making pull requests from master of your fork is discouraged. You should set
up a branch for your update. I will be updating khal, so I will create a
branch named khal:
git checkout -b khal upstream/master
Updating package
I will be demonstrating the process on the khal package. You should do this on
the package you want to update, the process is the same.
khal’s template at the time of writing this tutorial looks like this:
# Template file for 'khal'
pkgname=khal
version=0.11.2
revision=2
build_style=python3-module
_rundeps="python3-click python3-click-log python3-configobj python3-dateutil
python3-icalendar python3-pytz python3-tzlocal python3-urwid python3-xdg
python3-atomicwrites"
hostmakedepends="python3-setuptools_scm python3-Sphinx python3-sphinxcontrib $_rundeps"
depends="$_rundeps"
checkdepends="python3-pytest python3-freezegun python3-hypothesis vdirsyncer $depends"
short_desc="Command-line calendar build around CalDAV"
maintainer="Anachron <gith@cron.world>"
license="MIT"
homepage="http://lostpackets.de/khal/"
changelog="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/pimutils/khal/master/CHANGELOG.rst"
distfiles="${PYPI_SITE}/k/khal/khal-${version}.tar.gz"
checksum=8fb8d89371e53e2235953a0765e41b97e174848a688d63768477576d03f899ba
make_check=ci-skip # some tests fail when running as root
post_install() {
vlicense COPYING
local _pypath="${DESTDIR}/${py3_sitelib}"
if [ "$CROSS_BUILD" ]; then
_pypath="${_pypath}:${XBPS_CROSS_BASE}/${py3_lib}"
fi
for sh in bash fish zsh; do
PYTHONPATH="${_pypath}" _KHAL_COMPLETE="${sh}_source" \
"${DESTDIR}/usr/bin/khal" > "khal.${sh}"
vcompletion "khal.${sh}" $sh
done
vsconf khal.conf.sample
PYTHONPATH="${_pypath}" make -C doc man
vman doc/build/man/khal.1
}
The template uses version 0.11.2. There is a newer version 0.11.3:
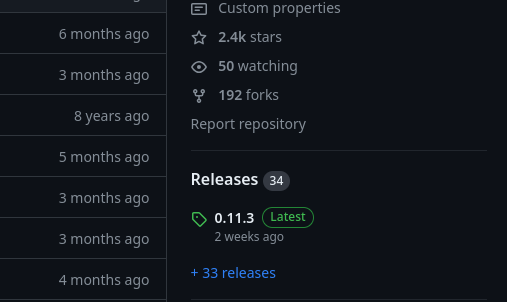
We first have to modify the version variable to match version 0.11.3:
# Template file for 'khal'
pkgname=khal
version=0.11.3
revision=2
build_style=python3-module
_rundeps="python3-click python3-click-log python3-configobj python3-dateutil
python3-icalendar python3-pytz python3-tzlocal python3-urwid python3-xdg
python3-atomicwrites"
hostmakedepends="python3-setuptools_scm python3-Sphinx python3-sphinxcontrib $_rundeps"
depends="$_rundeps"
checkdepends="python3-pytest python3-freezegun python3-hypothesis vdirsyncer $depends"
short_desc="Command-line calendar build around CalDAV"
maintainer="Anachron <gith@cron.world>"
license="MIT"
homepage="http://lostpackets.de/khal/"
changelog="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/pimutils/khal/master/CHANGELOG.rst"
distfiles="${PYPI_SITE}/k/khal/khal-${version}.tar.gz"
checksum=8fb8d89371e53e2235953a0765e41b97e174848a688d63768477576d03f899ba
make_check=ci-skip # some tests fail when running as root
post_install() {
vlicense COPYING
local _pypath="${DESTDIR}/${py3_sitelib}"
if [ "$CROSS_BUILD" ]; then
_pypath="${_pypath}:${XBPS_CROSS_BASE}/${py3_lib}"
fi
for sh in bash fish zsh; do
PYTHONPATH="${_pypath}" _KHAL_COMPLETE="${sh}_source" \
"${DESTDIR}/usr/bin/khal" > "khal.${sh}"
vcompletion "khal.${sh}" $sh
done
vsconf khal.conf.sample
PYTHONPATH="${_pypath}" make -C doc man
vman doc/build/man/khal.1
}
A new version of a package should have revision always set to 1:
# Template file for 'khal'
pkgname=khal
version=0.11.3
revision=1
build_style=python3-module
_rundeps="python3-click python3-click-log python3-configobj python3-dateutil
python3-icalendar python3-pytz python3-tzlocal python3-urwid python3-xdg
python3-atomicwrites"
hostmakedepends="python3-setuptools_scm python3-Sphinx python3-sphinxcontrib $_rundeps"
depends="$_rundeps"
checkdepends="python3-pytest python3-freezegun python3-hypothesis vdirsyncer $depends"
short_desc="Command-line calendar build around CalDAV"
maintainer="Anachron <gith@cron.world>"
license="MIT"
homepage="http://lostpackets.de/khal/"
changelog="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/pimutils/khal/master/CHANGELOG.rst"
distfiles="${PYPI_SITE}/k/khal/khal-${version}.tar.gz"
checksum=8fb8d89371e53e2235953a0765e41b97e174848a688d63768477576d03f899ba
make_check=ci-skip # some tests fail when running as root
post_install() {
vlicense COPYING
local _pypath="${DESTDIR}/${py3_sitelib}"
if [ "$CROSS_BUILD" ]; then
_pypath="${_pypath}:${XBPS_CROSS_BASE}/${py3_lib}"
fi
for sh in bash fish zsh; do
PYTHONPATH="${_pypath}" _KHAL_COMPLETE="${sh}_source" \
"${DESTDIR}/usr/bin/khal" > "khal.${sh}"
vcompletion "khal.${sh}" $sh
done
vsconf khal.conf.sample
PYTHONPATH="${_pypath}" make -C doc man
vman doc/build/man/khal.1
}
The package won’t build now because the source archive has changed. xbps-src
checksums the source archive. Because it has changed, the check will fail.
The xtools package includes a handy helper for calculating the checksums:
xgensum. You just have to run:
xgensum -i khal
and it will automatically download the archive and generate the sha256sum. The
-i flag will modify the template in place and it will overwrite the checksum
variable.
Note that xgensum will output this:
=> xbps-src: updating software in / masterdir...
=> xbps-src: cleaning up / masterdir...
=> khal-0.11.3_1: running do-fetch hook: 00-distfiles ...
=> WARNING: khal-0.11.3_1: wrong checksum found for khal-0.11.3.tar.gz - purging
/host/sources/khal-0.11.3/khal-0.11.3.tar.gz
=> khal-0.11.3_1: fetching distfile 'khal-0.11.3.tar.gz' from 'https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/source/k/khal/khal-0.11.3.tar.gz'...
khal-0.11.3.tar.gz: [192KB 2%] 49KB/s ETA: 00m00s
khal-0.11.3.tar.gz: 192KB [avg rate: 2361KB/s]
=> khal-0.11.3_1: verifying checksum for distfile 'khal-0.11.3.tar.gz'...
=> ERROR: SHA256 mismatch for 'khal-0.11.3.tar.gz:'
a8ccbcc43fc1dbbc464e53f7f1d99cf15832be43a67f38700e535d99d9c1325e
=> ERROR: khal-0.11.3_1: couldn't verify distfiles, exiting...
The last three lines are highlighted in red. You don’t have to worry about the
ERROR, this is the intended behaviour of xgensum.
The package should be usable now. You can now build it with
./xbps-src pkg khal
If it doesn’t build, there is a possibility that there has been a breaking
change in the update (I am speaking generally, khal specifically should
build). This is a possibility that I’ve mentioned at the beginning of this page.
You should check the release notes on the GitHub Releases page or a changelog if
the project has one.
It might be necessary to modify the template to fix the build. There is no
universal way to fix these problems, but a general understanding of xbps-src
is helpful in these situations. I recommend you read the xbps-src packaging
tutorial.
xlint
You should always run xlint when finishing a package. It can find common
errors in templates and it enforces some stylistic choices used across
void-packages.
A package update should ideally not change xlint output.
xlint khal
should output nothing.
If it does output warnings, you should fix them. But if the template is complicated and the warning did occur before you have made the changes (you haven’t caused the warnings), it is tolerable to leave the warning be. You should make a comment about it in the pull request description.
Making a pull request
Contributing is described at Contributing. You
should already have a working clone of your fork, the upstream remote should
be set up and you should be on a non-default branch. You can skip these parts in
Contributing.
You should ensure that the branch is up to date.
To summarize, the process should look like this:
First
xbump khal
This will create the commit. It should look something like this:
> git show
commit c2728f03ff3db70bbd575143ae1801ca40fb2314
Author: meator <meator.dev@gmail.com>
Date: Sun Feb 25 12:00:00 2024 +0100
khal: update to 0.11.3.
diff --git a/srcpkgs/khal/template b/srcpkgs/khal/template
index d43a04bef73..f56d78ad9ff 100644
--- a/srcpkgs/khal/template
+++ b/srcpkgs/khal/template
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
# Template file for 'khal'
pkgname=khal
-version=0.11.2
-revision=2
+version=0.11.3
+revision=1
build_style=python3-module
_rundeps="python3-click python3-click-log python3-configobj python3-dateutil
python3-icalendar python3-pytz python3-tzlocal python3-urwid python3-xdg
@@ -15,7 +15,7 @@ license="MIT"
homepage="http://lostpackets.de/khal/"
changelog="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/pimutils/khal/master/CHANGELOG.rst"
distfiles="${PYPI_SITE}/k/khal/khal-${version}.tar.gz"
-checksum=8fb8d89371e53e2235953a0765e41b97e174848a688d63768477576d03f899ba
+checksum=a8ccbcc43fc1dbbc464e53f7f1d99cf15832be43a67f38700e535d99d9c1325e
make_check=ci-skip # some tests fail when running as root
post_install() {
Then you should push the changes:
# replace khal with your branch name
git push -u origin khal
It will output a link that will open the pull request.
You should preferably ping the maintainer of the package by putting @name
(for example @meator) in the pull request description. This will issue a
notification to the maintainer. You don’t have to do this if the maintainer is
Orphaned <orphan@voidlinux.org>
If that is the case and you’re interested in the package (if you aren’t interested in it, why are you updating it?), you should consider adopting the package.
There are alternative ways of cloning. They are described at different ways of cloning.
This is briefly described in the remotes section of contributing (of this tutorial, not void-packages’ CONTRIBUTING)